Difference between revisions of "Triton"
(Added content.) |
(Updated orbital and physical parameters.) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
!bgcolor="lightsteelblue" colspan="2"|Planetary mean orbits | !bgcolor="lightsteelblue" colspan="2"|Planetary mean orbits | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |width="30%"|Epoch||align="right" width="50%"| | + | |width="30%"|Epoch||align="right" width="50%"|1989.6466 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |width="30%"|Semimajor axis (a)||align="right" width="50%"| | + | |width="30%"|Semimajor axis (a)||align="right" width="50%"|357 800 000 m |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |width="30%"|Eccentricity (e)||align="right" width="30%"|0. | + | |width="30%"|Eccentricity (e)||align="right" width="30%"|0.0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |width="30%"|Inclination (i)||align="right" width="30%"| | + | |width="30%"|Inclination (i)||align="right" width="30%"|156.8602026° <br> (2.737727 radian) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |width="30%"|Longitude of the ascending node (LAN, ☊)||align="right" width="30%"| | + | |width="30%"|Longitude of the ascending node (LAN, ☊)||align="right" width="30%"|172.4316484° <br> (3.0095 radian) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |width="30%"|Longitude of periapsis (ϖ)||align="right" width="30%"| | + | |width="30%"|Longitude of periapsis (ϖ)||align="right" width="30%"|156.4747739° <br> (2.731 radian) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |width="30%"|Mean longitude (L)||align="right" width="30%"| | + | |width="30%"|Mean longitude (L)||align="right" width="30%"|61.25491788° <br> (1.0691 radian) |
|- | |- | ||
!bgcolor="lightsteelblue" colspan="2"|Selected physical parameters | !bgcolor="lightsteelblue" colspan="2"|Selected physical parameters | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |width="30%"|Mean radius||align="right" width="30%"| | + | |width="30%"|Mean radius||align="right" width="30%"|1353400 m |
|- | |- | ||
|width="30%"|Mass||align="right" width="30%"|2.14×10<sup>22</sup> kg | |width="30%"|Mass||align="right" width="30%"|2.14×10<sup>22</sup> kg | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |width="30%"|Note||align="right" width="30%"|*Elements given are from Triton.cfg ( | + | |width="30%"|Note||align="right" width="30%"|*Elements given are from Triton.cfg (triton.zip) |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 11:14, 2 September 2024
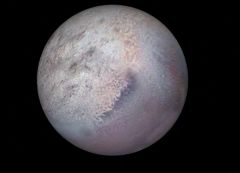
Triton is the largest moon of Neptune and the seventh largest moon in the Solar System.It the only moon of Neptune that has reached hydrostatic equilibrium and it has a thin atmosphere. Triton's orbit is retrograde.
Triton was discovered by William Lassell on 10 October 1846, just 17 days after Neptune was discovered.
Triton in Orbiter
Triton was introduced to Orbiter with the add-on uranus-neptune-moons.zip in October 2002. In April 2003 Rolf Keibel released triton.zip with two different atmospheres as options.
| Add-on | Source | Version | Author | Type | Release Date | Compatibility | Wiki article |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triton | AVSIM | Rolf Keibel | Scenery | 25 April 2003 | |||
| Orbiter 2003-P2 | O-F Resources | 031217 | martins | Orbiter Download | 17 December 2003 | Orbiter 2003-P2 | |
| Orbiter 2003-P1 | O-F Resources | 031105 | martins | Orbiter Download | 5 November 2003 | ||
| Uranus / Neptune Moons Addon | AVSIM | Robert Stettner (Foxtrot) | Scenery | 12 October 2002 | |||
See also
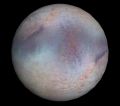
Triton as seen by Voyager 2
| Neptune's natural satellites |
|---|
| Named satellites:
Despina | Galatea | Halimede | Hippocamp | Laomedeia | Larissa | Naiad | Nereid | Neso | Proteus | Psamathe | Sao | Thalassa | Triton Numbered Satellites: |
| See also: Pronunciation key | rings of Neptune |
| edit The Solar System | |
|---|---|
| Central star |
Sun (Sol) |
| Planets |
Mercury - Venus - Earth - Mars - Jupiter - Saturn - Uranus - Neptune |
| Natural satellites |
Moon - Phobos - Deimos - Io - Europa - Ganymede - Titan - more... |
| Add-ons |
Planets - Dwarf Planets - Small objects - Natural satellites - Alternative star systems |
 | This natural satellite related article is a stub. You can help Orbiterwiki by expanding it.
|