Difference between revisions of "Phobos"
(Added infobox.) |
(Added link.) |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
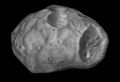
Phobos is the larger of the two moons and is only 27 kilometres in diameter. This is about as far as a car can travel on the highway in 15 minutes. It is covered with craters, as [[Earth]]'s moon is. | Phobos is the larger of the two moons and is only 27 kilometres in diameter. This is about as far as a car can travel on the highway in 15 minutes. It is covered with craters, as [[Earth]]'s moon is. | ||
| − | It is named after the god [[Phobos]] in Greek mythology. Its name means "fear". Phobos was discovered by [[w:Asaph Hall|Asaph Hall]] on 18 August 1877. | + | It is named after the god [[w:Phobos (mythology)|Phobos]] in Greek mythology. Its name means "fear". Phobos was discovered by [[w:Asaph Hall|Asaph Hall]] on 18 August 1877. |
Phobos is trapped in tidal drag, with its orbit lowering roughly 1.8 meters per century. In about 50 million years, Phobos will reach the Roche limit, where it is likely to be torn apart. Some fragments will fall on Mars and some will form a planetary ring or rings around Mars. | Phobos is trapped in tidal drag, with its orbit lowering roughly 1.8 meters per century. In about 50 million years, Phobos will reach the Roche limit, where it is likely to be torn apart. Some fragments will fall on Mars and some will form a planetary ring or rings around Mars. | ||
Revision as of 11:00, 1 August 2024
Phobos (or Mars I) is one of Mars' moons. The other is Deimos.
Phobos is the larger of the two moons and is only 27 kilometres in diameter. This is about as far as a car can travel on the highway in 15 minutes. It is covered with craters, as Earth's moon is.
It is named after the god Phobos in Greek mythology. Its name means "fear". Phobos was discovered by Asaph Hall on 18 August 1877.
Phobos is trapped in tidal drag, with its orbit lowering roughly 1.8 meters per century. In about 50 million years, Phobos will reach the Roche limit, where it is likely to be torn apart. Some fragments will fall on Mars and some will form a planetary ring or rings around Mars.
Phobos in Orbiter
Phobos was introduced to Orbiter with the release of Orbiter 2002.
| Add-on | Source | Version | Author | Type | Release Date | Compatibility | Wiki article |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orbiter 2002 | O-F Resources | 020419 | martins | Orbiter Download | 19 April 2002 | Orbiter 2002 | |
| Orbiter 2001 | O-F Resources | 010503 | martins | Orbiter Download | 3 May 2001 | Orbiter 2001 | |
See Also
| edit The Solar System | |
|---|---|
| Central star |
Sun (Sol) |
| Planets |
Mercury - Venus - Earth - Mars - Jupiter - Saturn - Uranus - Neptune |
| Natural satellites |
Moon - Phobos - Deimos - Io - Europa - Ganymede - Titan - more... |
| Add-ons |
Planets - Dwarf Planets - Small objects - Natural satellites - Alternative star systems |
 | This natural satellite related article is a stub. You can help Orbiterwiki by expanding it. |