216 Kleopatra
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| 216 Kleopatra | |
|---|---|
| |
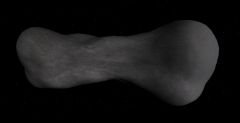
| 216 Kleopatra from AsteroidPack_v1.00.zip in Orbiter 2002P3 | |
| Designation | |
| Name | 216 Kleopatra |
| Reference body | Sun |
| Planetary mean orbits | |
| Epoch | 2006 |
| Semimajor axis (a) | 417 984 360 287.592 m |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.25156771162119 |
| Inclination (i) | 13.13670991° (0.229278840724192 radian) |
| Longitude of the ascending node (LAN, ☊) | 215.6635692° (3.76403935984912 radian) |
| Longitude of periapsis (ϖ) | 384.8684456° (6.89175448860117 radian) |
| Mean longitude (L) | 520.9843206° (9.09289174498727 radian) |
| Selected physical parameters | |
| Mean radius | 130670 km |
| Mass | 1.989×1018 kg |
| Rotation elements | |
| SidRotPeriod | 19386 seconds (5.385 hours) |
| SidRotOffset | 0 |
| Obliqutiy | 0 |
| LAN | 0 |
| Note | *Elements given are from 216 Kleopatra.cfg (AsteroidPack_v1.00.zip) |
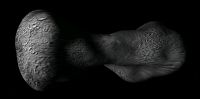
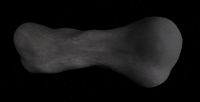
216 Kleopatra is a large asteroid shape sorta like a dumbbell. It was discovered by Johann Palisa on 10 April 1880 and was named for Cleopatra.
216 Kleopatra in Orbiter
216 Kleopatra was first introduced with the release of MainBeltAsteroids051403.zip in May 2003.
Note that the landing surface as given in the config file is spherical, but the visual of these bodies are not, if you land, you will likely be above or below the visual surface.
| Add-on | Source | Version | Author | Type | Release Date | Compatibility | Wiki article |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asteroid Pack 1.00 | O-F Resources | 2004-11-21 | Nighthawke | Scenery | 21 November 2004 | ||
| Main Belt Asteroids v1.0 | O-F Resources | v1.0 | Unknown OHM Addon Developer | Scenery | 14 May 2003 | ||
See also
Gallery
| edit The Solar System | |
|---|---|
| Central star |
Sun (Sol) |
| Planets |
Mercury - Venus - Earth - Mars - Jupiter - Saturn - Uranus - Neptune |
| Natural satellites |
Moon - Phobos - Deimos - Io - Europa - Ganymede - Titan - more... |
| Add-ons |
Planets - Dwarf Planets - Small objects - Natural satellites - Alternative star systems |