| Hydra
|
|
| Hydra from Nix-Hydra.zip in Orbiter 2006P1
|
| Designation
|
| Name |
Hydra
|
| Reference body |
134340 Pluto
|
| Number of satellites |
|
| Planetary mean orbits
|
| Epoch |
38.8, J39
|
| Semimajor axis (a) |
78400000 m
|
| Eccentricity (e) |
0.0051
|
| Inclination (i) |
19.480565034448°
(0.34 radian)
|
| Longitude of the ascending node (LAN, ☊) |
53.0076487827642°
(0.925158 radian)
|
| Longitude of periapsis (ϖ) |
224.066662237591°
(3.910701 radian)
|
| Mean longitude (L) |
238.928729077048°
(4.170093 radian)
|
| Selected physical parameters
|
| Mean radius |
253000 m
|
| Mass |
2×1020 kg
|
| Sidereal rotation period |
22994.1 sec (6.38725 hours)
|
| SidRotOffset |
0
|
| Obliquity |
0° (0 radian)
|
| Note |
*Elements given are from Hyra.cfg (Nix-Hydra.zip)
|
Hydra is the second largest natural satellite of Pluto after Charon. It was discovered in images by the Hubble Space Telescope in May 2005 and was named after Hydra, the nine-headed serpent in Greek mythology.
Hydra in Orbiter
Hydra was introduced to Orbiter with the release of Nix-Hydra.zip in August 2009.
| Orbiter versions and add-ons which include Hydra
|
| Add-on |
Source |
Version |
Author |
Type |
Release Date |
Compatibility |
Wiki article
|
| Pluto Minor Moons |
O-F Resources |
2009-08-21 |
DagoO |
Scenery |
22 August 2009 |
|
|
Gallery
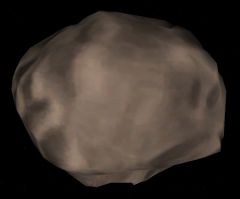
Hydra from Nix-Hydra.zip in Orbiter 2006P1
Image of Hydra from the New Horizons spacecraft taken July 2015
from Wikimedia Commons
Pluto and three satellites taken by Hubble
from Wikimedia Commons in 2005